Introduction
Fiberglass grating has emerged as a revolutionary material in industrial flooring, platforms, and walkways across numerous sectors. This versatile product offers a compelling alternative to traditional metal gratings, with distinctive properties that make it ideal for challenging environments. According to industry reports, the global fiberglass grating market is projected to reach $421 million by 2027, with a CAGR of 5.8% from 2020 to 2027, highlighting its growing significance. Whether you’re upgrading existing infrastructure or planning new installations, understanding what fiberglass grating is and its applications can help you make informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide covers everything from basic definitions to installation tips to ensure you select the right product for your specific needs.
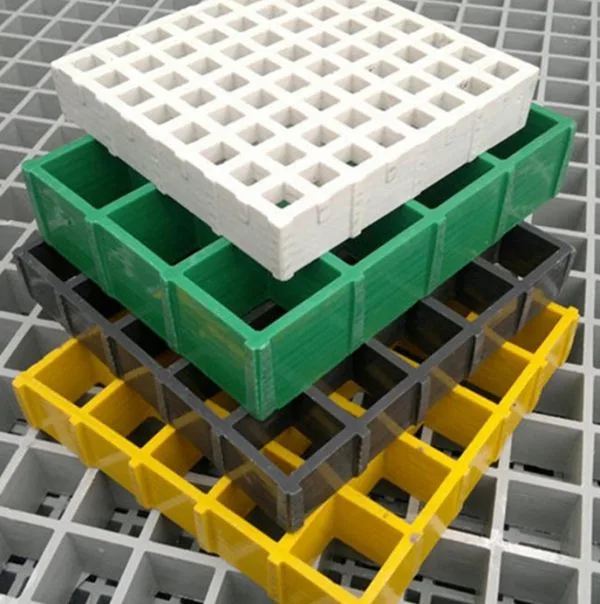
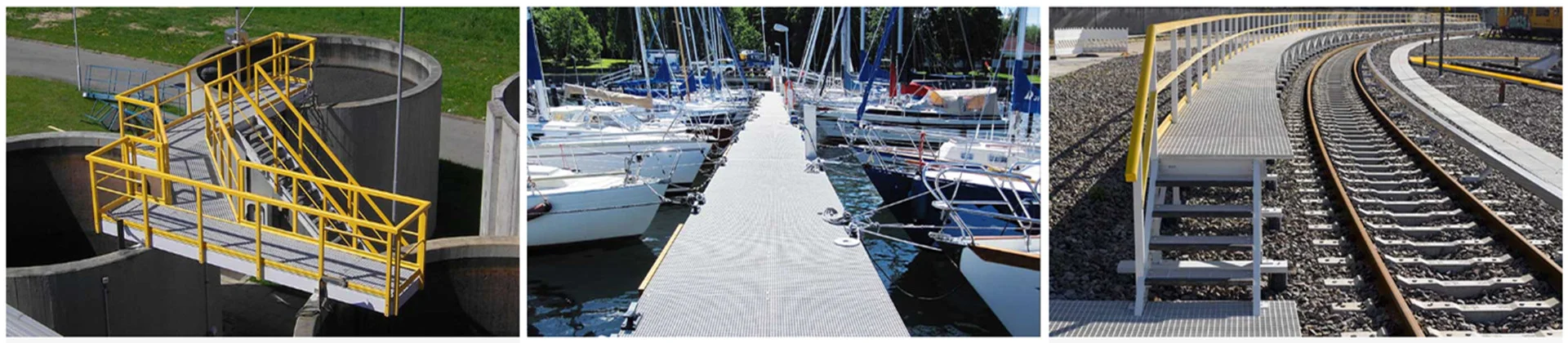
what is fiberglass grating
What Is Fiberglass Grating?
Definition and Basic Composition
Fiberglass grating, also known as FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) grating, is a type of open grid flooring manufactured using glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix. This composite material combines fiberglass reinforcement with thermosetting resins such as polyester, vinyl ester, or phenolic to create rigid, durable panels with open spaces. The standard composition typically includes:
- Glass fiber reinforcement (50-65%)
- Thermosetting resin system (30-45%)
- Additives for UV protection, fire resistance, and color (5-10%)
The resulting material delivers exceptional strength while remaining significantly lighter than traditional metal alternatives. As noted by the American Composites Manufacturers Association, fiberglass components typically weigh 70-80% less than their steel counterparts while maintaining comparable strength characteristics.
Manufacturing Process
Fiberglass grating is produced through two primary manufacturing methods, each yielding products with unique characteristics:
- Molding Process: This method involves placing continuous strand glass fiber reinforcements in a mold, then injecting thermosetting resin under pressure. The material is cured at high temperatures to create a one-piece, monolithic panel with integral cross-members and a meniscus (slightly concave) top surface for slip resistance.
- Pultrusion Process: This continuous manufacturing technique pulls glass fiber reinforcements through a resin bath, then through heated dies that shape and cure the material. The resulting pultruded profiles are assembled and bonded to create grating panels with uniform composition and directional strength.
According to manufacturing experts at Bedford Reinforced Plastics, the pultrusion process creates products with up to 40% higher tensile strength in the lengthwise direction compared to molded alternatives, making material selection crucial depending on application requirements.
Types of Fiberglass Grating
Molded Fiberglass Grating
Molded grating features a distinctive square or rectangular mesh pattern with integral nodes at intersections. Key characteristics include:
- Bi-directional strength (equal load capacity in both directions)
- Superior corrosion resistance due to higher resin content
- Available in various panel sizes, typically 3′ × 10′ or 4′ × 8′
- Standard depths ranging from 3/4″ to 2″
- Load-bearing capacities from 50 to 300 psf (pounds per square foot)
Industry data shows molded grating remains the most widely used type, accounting for approximately 65% of all fiberglass grating installations due to its versatility and balanced performance characteristics.
Pultruded Fiberglass Grating
Pultruded grating consists of continuous bearing bars in one direction connected by cross-rods. Notable features include:
- Unidirectional strength (higher load capacity in the bearing bar direction)
- Higher glass content providing superior tensile strength
- Available in various panel sizes, typically 3′ × 20′ or 4′ × 20′
- Standard depths from 1″ to 4″
- Load-bearing capacities from 100 to 500 psf
A 2021 study by Composite Materials Today found that pultruded grating experiences approximately 30% less deflection under load than comparable molded products, making it ideal for high-load applications.
Mini-Mesh Grating
Mini-mesh is a specialized variation of molded grating with smaller openings, offering:
- Mesh spacings as small as 1/2″ × 1/2″
- Enhanced safety for small items or tools
- Improved comfort for pedestrian traffic
- Ideal for laboratory floors, walkways, and areas where small objects are handled
Key Benefits of Fiberglass Grating
Corrosion Resistance
One of the most significant advantages of fiberglass grating is its exceptional resistance to chemical attack. Unlike traditional materials:
- Resistant to over 300 different chemicals and compounds
- Will not deteriorate in salt water environments
- Unaffected by acids, alkalis, and most solvents
- No galvanic reaction when in contact with dissimilar metals
The American Society of Civil Engineers reports that facilities using fiberglass components in corrosive environments can reduce maintenance costs by up to 40% compared to metal alternatives, with service lives extending beyond 30 years in many applications.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Fiberglass grating offers remarkable structural performance while remaining lightweight:
- Typically 70-80% lighter than steel grating
- 30-40% lighter than aluminum alternatives
- Reduces installation costs and structural requirements
- Allows for easier handling during installation and maintenance
This weight advantage translates to tangible benefits, with installation crews reporting up to 50% faster completion times compared to steel grating projects, according to a 2022 industry survey by Industrial Flooring Digest.
Safety Features
Modern fiberglass grating incorporates numerous safety enhancements:
- Non-conductive properties protect against electrical hazards
- Available with grit-top surfaces providing slip resistance even when wet
- Fire-retardant formulations meeting ASTM E84 Class 1 flame spread rating
- No sparking risk in explosive environments
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has documented a 35% reduction in slip-and-fall incidents in facilities that upgraded to grit-top fiberglass grating from traditional steel alternatives.
Low Maintenance Requirements
Once installed, fiberglass grating requires minimal ongoing maintenance:
- No painting or coating required
- Will not rust, rot, warp, or delaminate
- Color-stabilized to resist fading from UV exposure
- Simple cleaning with water and mild detergent
Maintenance engineers report annual upkeep costs averaging 70-85% lower than metal gratings over a 15-year service period, primarily due to eliminated repainting and rust remediation needs.
Common Applications of Fiberglass Grating
Industrial Environments
Fiberglass grating has become the standard in many industrial settings:
- Chemical processing plants
- Pulp and paper mills
- Food processing facilities
- Manufacturing floors
- Access platforms and walkways
The material’s durability in harsh conditions makes it particularly valuable in environments with chemical exposure, high humidity, or frequent washing requirements.
Marine and Offshore
Marine applications represent over 25% of the fiberglass grating market, with installations including:
- Boat docks and marinas
- Offshore drilling platforms
- Ship decks and gangways
- Fish processing facilities
- Cooling tower platforms
According to the International Marine Organization, fiberglass materials in offshore applications show approximately 3-5 times the service life of galvanized steel, even in harsh saltwater environments.
Chemical Processing Facilities
The chemical resistance of fiberglass grating makes it ideal for:
- Chemical storage areas
- Processing units
- Laboratory floors
- Containment areas
- Waste treatment facilities
A Chemical Processing Industry report indicates that 78% of chemical processing facilities now specify fiberglass components as their preferred option for new construction and renovation projects due to long-term cost savings.
Water Treatment Plants
Water and wastewater treatment facilities extensively use fiberglass grating for:
- Aeration basin covers
- Walkways around clarifiers
- Access platforms over treatment tanks
- Pump station flooring
- Filter gallery walkways
The material’s resistance to chlorine, ozone, and treatment chemicals provides significant advantages, with facilities reporting service lives exceeding 25 years in properly specified applications.
Important Factors to Consider Before Purchasing
Load Requirements
Determining the correct load capacity is critical for safe, efficient installations:
- Uniform load: The distributed weight across the panel (expressed in psf)
- Concentrated load: Point loads from equipment or heavy objects
- Deflection limitations: Maximum allowable bending under load
- Dynamic loads: Moving equipment or vibration considerations
Engineering best practices recommend selecting grating with a minimum safety factor of 3:1 for typical walkway applications and 5:1 for critical equipment support platforms.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors significantly influence material selection:
- Chemical exposure: Types and concentrations of chemicals present
- Temperature extremes: Operating temperature range
- UV exposure: Direct sunlight and weather exposure
- Fire risk: Need for flame-retardant formulations
- Electrical hazards: Requirement for non-conductive properties
For extreme environments, specialty resins such as vinyl ester (offering superior chemical resistance) or phenolic (providing enhanced fire performance) may be specified.
Compliance and Regulations
Ensure your selection meets all applicable standards:
- OSHA requirements for walkways and platforms
- ADA accessibility guidelines where applicable
- ASTM testing standards for load capacity and fire resistance
- Local building codes and industry-specific regulations
- ANSI standards for slip resistance
A recent survey found that 24% of operations managers reported compliance issues after installation due to inadequate pre-purchase evaluation of regulatory requirements.
Cost Considerations
While initial cost is important, total life-cycle analysis provides a more accurate picture:
- Material costs (typically 15-30% higher than steel initially)
- Installation costs (generally 20-40% lower due to reduced weight)
- Maintenance expenses (70-85% lower over service life)
- Replacement frequency (2-3 times longer service life in corrosive environments)
- Disposal/recycling considerations
Industry calculations indicate that despite higher upfront costs, fiberglass grating typically reaches cost break-even with steel alternatives within 3-5 years in corrosive environments, with significant savings thereafter.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation ensures optimal performance and longevity:
- Use recommended fasteners (typically 316 stainless steel clips or hold-downs)
- Maintain proper support spacing according to load requirements
- Allow for thermal expansion in large installations (approximately 1/8″ per 10°F temperature change per 10 feet)
- Use appropriate cutting methods (abrasive blade or diamond-tipped tools)
- Seal cut edges with resin to maintain corrosion resistance
Professional installers recommend providing at least 1.5″ of bearing surface on all supported edges and using proper respiratory protection when cutting fiberglass materials.
Long-term Maintenance
While minimal, some maintenance practices extend service life:
- Regular cleaning with water and mild detergent
- Periodic inspection for damage or wear
- Immediate repair of damaged areas to prevent progression
- Avoiding pressure washing exceeding 2,500 psi
- Removing debris from grid openings to maintain drainage
Conclusion
Fiberglass grating represents a significant advancement in industrial flooring technology, offering compelling advantages in corrosion resistance, weight, safety, and long-term cost efficiency. By understanding what fiberglass grating is and carefully evaluating the types, benefits, and applications discussed in this guide, you can make informed purchasing decisions tailored to your specific requirements.
Remember to consider all relevant factors—from load requirements and environmental conditions to compliance standards and lifecycle costs—to ensure you select the optimal product for your application. With proper specification and installation, fiberglass grating provides exceptional performance and durability for decades of reliable service.
We encourage you to share your experiences with fiberglass grating in the comments section below or contact us with specific questions about your application requirements. If you found this guide helpful, please share it with colleagues who might benefit from this information as they evaluate industrial flooring options.




























