Introduction
In the world of modern engineering and construction, materials like steel and aluminum have long dominated the landscape. However, the rise of innovative materials such as reinforced fiberglass angle is reshaping the industry. Known for its exceptional strength, durability, and versatility, this material is fast becoming a preferred choice for numerous applications, from construction frameworks to industrial equipment. But what makes it so unique? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about reinforced fiberglass angles, including their properties, applications, and benefits.
reinforced fiberglass angle
What is a Reinforced Fiberglass Angle?
Reinforced fiberglass angles are structural components made from a combination of fiberglass and resin, molded into an L-shaped profile. This composite material offers a superior alternative to traditional construction materials, combining lightweight properties with remarkable strength.
Fiberglass angles are produced through processes such as pultrusion, which ensures consistent quality and performance. Unlike steel or aluminum, these angles are corrosion-resistant, making them ideal for harsh environments.
Key Properties of Reinforced Fiberglass Angle
Reinforced fiberglass angles are known for their exceptional performance, thanks to the following properties:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Despite being lightweight, fiberglass angles can withstand significant loads, making them ideal for structural applications. - Corrosion Resistance
Unlike metal components, these angles do not rust or deteriorate in wet or chemically aggressive environments. - Electrical Insulation
Fiberglass is a natural insulator, providing safety and efficiency in electrical applications. - Thermal Stability
While fiberglass performs well in most temperature ranges, certain resins enhance its heat resistance for specialized applications.
Manufacturing Process of Reinforced Fiberglass Angles
The pultrusion method is the primary technique used to create reinforced fiberglass angles. This involves:
- Pulling continuous strands of fiberglass through a resin bath.
- Shaping the material into a desired profile using a heated die.
- Curing and cutting the final product to precise dimensions.
The quality of the resin and fiberglass directly impacts the performance of the finished product. High-grade materials ensure better strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors.
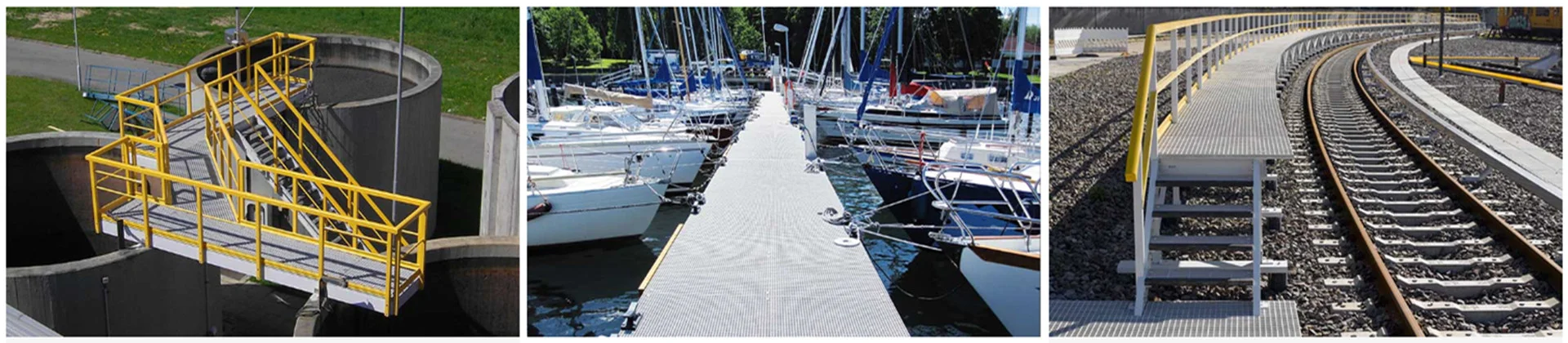
Common Applications of Reinforced Fiberglass Angles
Reinforced fiberglass angles are incredibly versatile. Some of their most common applications include:
- Construction
- Frameworks for bridges and buildings.
- Support structures for roofing and flooring systems.
- Electrical Industry
- Cable trays and conduits.
- Insulating components for substations and transformers.
- Marine and Chemical Environments
- Anti-corrosive structures for docks and offshore platforms.
- Chemical storage tanks and pipelines.
Benefits of Using Reinforced Fiberglass Angles
- Lightweight Yet Durable
Fiberglass angles offer high performance without adding significant weight to structures, reducing transportation and handling costs. - Cost-Effectiveness
Although the initial investment might be higher, the long-term savings in maintenance and replacements make them a cost-effective choice. - Environmental Benefits
These materials contribute to sustainable construction practices due to their recyclability and lower energy requirements during production.
Comparing Reinforced Fiberglass Angles with Steel and Aluminum
When choosing materials for construction or industrial projects, fiberglass angles stand out in several ways:
| Property | Fiberglass Angle | Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Moderate |
| Electrical Insulation | Yes | No | Limited |
| Maintenance | Low | High | Moderate |
Installation and Handling Tips
For the best results, consider the following when working with reinforced fiberglass angles:
- Cutting and Drilling: Use carbide-tipped tools for clean cuts and holes.
- Safety Gear: Wear gloves and masks to prevent irritation from fiberglass particles.
- Fixing: Secure the angles using appropriate fasteners designed for composite materials.
Maintenance and Longevity
Fiberglass angles require minimal maintenance, making them an excellent investment for long-term applications. Basic care includes:
- Routine Cleaning: Use mild detergents to clean surfaces and remove debris.
- Inspection: Regularly check for minor cracks or damages, especially in high-stress environments.
- Repairs: Apply epoxy resin to fix minor cracks or chips, extending the lifespan of the material.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reinforced fiberglass angles align with environmentally friendly practices due to their:
- Recyclability: Components can often be reused or recycled into new products.
- Energy Efficiency: The production process consumes less energy compared to metals like steel and aluminum.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many benefits, reinforced fiberglass angle has some challenges:
- Higher Upfront Cost: Initial expenses can be more than traditional materials.
- Heat Resistance: Standard fiberglass may degrade under extreme heat, though advanced resins can address this issue.
Innovations in Reinforced Fiberglass Technology
Advancements in technology are continually enhancing the performance of fiberglass angles. For example:
- Enhanced Resins: Improved chemical formulations increase heat resistance and durability.
- Advanced Pultrusion Methods: New techniques allow for more precise manufacturing and greater customization.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations
- Industrial Cooling Towers: Fiberglass angles have replaced metal supports, offering long-term corrosion resistance.
- Offshore Platforms: Their durability in saltwater conditions makes them indispensable for marine applications.
Future Trends in Fiberglass Applications
As industries strive for more sustainable and efficient solutions, the demand for reinforced fiberglass materials is expected to grow. Emerging trends include:
- Integration with Smart Technologies: Sensors embedded within fiberglass structures for real-time monitoring.
- Expansion in Renewable Energy: Use in wind turbines and solar panel supports.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What makes reinforced fiberglass angles stronger than steel?
Their unique composite structure offers high tensile strength without the weight of steel. - Can fiberglass angles be used outdoors?
Yes, their corrosion-resistant properties make them ideal for outdoor use. - How do I cut reinforced fiberglass angles?
Use specialized tools like carbide-tipped saws for precise cuts. - Are reinforced fiberglass angles eco-friendly?
Yes, they are recyclable and require less energy to produce compared to metals. - What industries commonly use fiberglass angles?
Construction, marine, chemical, and electrical industries are leading users. - What is the lifespan of a reinforced fiberglass angle?
With proper care, they can last for decades, even in harsh environments.
Conclusion
Reinforced fiberglass angles combine strength, durability, and sustainability, making them a game-changing material for various industries. Their lightweight yet robust nature, coupled with corrosion resistance and minimal maintenance needs, positions them as a superior alternative to traditional materials like steel and aluminum.
If you’re looking to enhance your next project with a reliable, future-proof solution, consider investing in reinforced fiberglass angles—they just might be the material you’ve been searching for.




























