In the construction industry, steel is often dealt with, such as two kinds of steel used in the market: I-beam and h-beam. You may have such doubts: what is the difference between I-beam and h-beam? Some people think that I-beam and h-beam are the same quality steel, and there is no difference, but Unicomposite tells you the difference between I-beam and h-beam, as well as the different performance and application characteristics of the two. Only by understanding the difference between I-beam and h-beam, can you choose suitable steel when choosing steel.
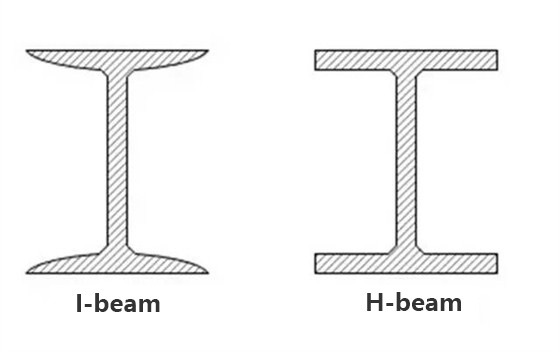
I-beams and H-beams
What is I-beam:
As the name implies, I-beam is an “I-shaped” section of steel. The inner surface of the upper and lower flanges has a gradient of 1:6, which makes the flange thin on the outside and thick on the inside. As a result, the section characteristics of the I-beam in the two main planes differ greatly, and it is difficult to give play to the strength characteristics of the steel in application. Although there are thickened I-beams in the market, the structure of I-beams has determined their short plate of torsion resistance.
What is H-beam:
H-beam is a widely used profile in today’s steel structure buildings, and it has many differences compared with I-beam.
- Flange, the inner surface of the flange has no inclination, and the upper and lower surfaces are parallel.
- The inside of the two outer edges of the H-beam has no slope and is straight.
- The cross-sectional properties of H-beams are significantly better than those of traditional I-beams, channel steels, and angle steels.
- H-beam is a kind of economical section and high-efficiency section with more optimized cross-sectional area distribution and a more reasonable strength-to-weight ratio. It is named after its section is the same as the English letter “H”. This makes the welding and splicing of H-beams easier than I-beams and has better mechanical properties per unit weight, which can save a lot of materials and construction time.
Summary: The I-beam section has good straight pressure and tensile resistance, but the section size cannot resist torsion because the wing plate is too narrow. H steel is the opposite, so both have their own advantages and disadvantages.
The difference between the application of I-beam and H-beam:
- Whether the I-beam is ordinary or light, due to the relatively high and narrow section size, the moment of inertia of the two main sleeves of the section is quite different. Therefore, it can generally only be used directly in the plane of its web. Bending members or forming lattice-type stress members. It is not suitable to use axial compression members or members that are perpendicular to the plane of the web and bend, which makes it very limited in the scope of application.
- H-beams are high-efficiency and economical cutting profiles (others include cold-formed thin-walled steels, profiled steel plates, etc.). Due to their reasonable cross-sectional shapes, they can make the steel perform better and improve the cutting capacity. Different from the ordinary I-shaped, the flange of the h-shaped steel is widened, and the inner and outer surfaces are usually parallel so that it is convenient to connect with other components with high-strength screws. Its size constitutes a fair series, and the models are complete, which is convenient for design and selection.
Steel is mainly used in the construction industry, and heavy industry and the laying of railway tracks are inseparable from the use of steel. By distinguishing the difference between I-beam and H-beam, we can choose the appropriate steel type according to the different needs of consumers. H-beam is more It is economical and practical, while I-beams are under strong pressure and light in texture. When choosing and designing buildings, the characteristics and differences of the two should be fully considered in order to play a better role.




























